I Have A Bump/Blister/Sore On My Penis, Should I Be Worried?

Published Jan 18, 2021
When you first notice unusual bumps, sores, or blisters on your penis, it can be disconcerting, to say the least. Your mind tends to think of worst-case scenarios immediately, which creates much more of a stir than there needs to be. This situation can be all the more concerning if you’re a sexually active man, but don’t worry. We’re here to dissect what it means when you have a bump, blister, or sore on your penis and what implications they could have on your health.
It might not be what you think.
When you see the slightest irregularities in your genital area, it’s easy for your thoughts to wander off to the most unwanted cause: sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, some tiny bumps are to be expected in this region; it’s actually quite common. The most likely reason behind these bumps is shaving and ingrown hairs, leading to folliculitis, the bacterial infection of a hair follicle.
Ingrown hairs are an extremely common outcome of shaving pubic hair in the genital area, which is very sensitive. In its early stages, folliculitis presents itself as a rash or a series of small red bumps or white to yellow-tipped pimples. Often, these cases are mild, requiring little to no intervention. But on the flipside, sores and blisters can be a whole different story.
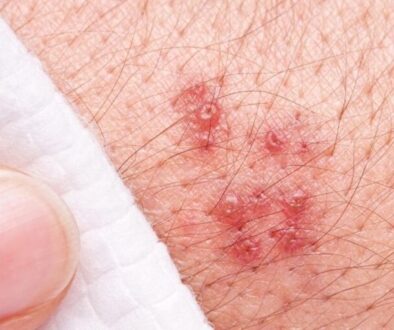
Blisters and Sores on Penis
As we’ve mentioned, small bumps or spots are not uncommon to find on and around your penis. However, a painful and discomforting sore or blister is a symptom of an underlying condition in the form of an STI or an immune system disorder.
What is a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
Sexually transmitted infections are infections you can contract when having unprotected sex with a partner. They can be transmitted in a variety of ways, including skin-to-skin contact, bodily fluid, and blood. If you find sores or blisters on your genital area, it could very well be due to an STI. Here’s a quick rundown of the most prevalent STIs that are likely causing your condition.

Genital Herpes
The first and one of the most widespread causes of genital blisters and sores is genital herpes. Genital herpes is a condition brought on by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This infection is a common one, where most people don’t even know they have it; most people with genital herpes show very mild symptoms if any at all.
Genital herpes is spread through unprotected sex with someone who has the infection. The worst part is that this can happen without any apparent symptoms or outbreaks either. An outbreak of this infection can cause painful pus-filled blisters to show up anywhere in your genital region, including your penis head, shaft, and base.
To accurately diagnose genital herpes, doctors use various physical exams and laboratory tests:
- Viral culture
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test
- Blood test
Like many viral infections, genital herpes does not have any cures, but there are ways to manage it:
- antiviral medication (acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir)
- washing affected areas with warm water and gentle soap
- adopting a healthy lifestyle and diet to work around the infection
- reducing stress as stress can aggravate symptoms
Genital Warts
Genital warts are another kind of viral STI brought about by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is the most common STI globally, affecting about 79 million Americans at present. While HPV usually goes away on its own without causing much of a stir, it can lead to more severe conditions like cancer and genital warts.
HPV is typically spread through sexual skin-to-skin contact, both oral and genital. Genital warts appear as small, flesh-colored bumps in the genital region. Diagnosing HPV usually requires two tests to be conducted, if either is inconclusive:
- Pap Test
- HPV Test
Treating your genital warts is not a requirement, especially if you don’t experience discomfort and pain. But if you’re experiencing itching, burning, and pain (all symptoms of genital warts), then you may opt for the following treatment options:
- Imiquimod
- Podophyllin and podofilox
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Sinecatechins
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection spread through sexual contact. It appears as a painless sore on your genitals and contact with which may spread the infection. After first contracting the infection, syphilis may remain dormant in your body for a number of years before resurfacing and causing problems.
The following tests may detect the presence of syphilis-causing bacteria in your body:
- Blood tests
- Cerebrospinal fluid
If you’re able to detect and diagnose syphilis early on, treatment is easy and straightforward. At all stages of this infection, penicillin is seen as the best treatment.
Chancroid
Chancroid is another sexually-transmitted bacterial infection that causes open sores to appear on and around your genitals. You should feel relieved that global incidence has declined significantly, especially in the United States.
Being an STI, you are at risk of contracting this infection if you’re sexually active. This risk increases even more if you travel and visit countries where this infection has been detected, particularly countries in Africa and the Caribbean. Heterosexual males seem to be at greater risk of contracting the virus than anybody else.
Accurately diagnosing the infection will require a sample of the fluid draining from the sore. These samples are sent to a laboratory for extensive testing and analysis.
The following are known ways of treating chancroid:
- Antibiotics (azithromycin, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin)
- Surgery
Scabies
Scabies is one of the more grotesque conditions on this list, enough to make your skin crawl. This condition is caused by the infestation of the skin by the human itch mite; these mites dig into your skin where they eat skin cells and lay eggs. It’s more widespread than you think it is, affecting millions of people each year all over the world. It is technically not a sexually transmitted infection; however, it can be spread through sexual contact nonetheless. You can contract scabies when you come into close physical contact with someone who has the condition.
Symptoms can include itching, pain, and sores appearing anywhere on your body. Scabies can easily be misdiagnosed as eczema or atopic dermatitis, as they produce similar symptoms. A biopsy may be required to examine the infected skin under a microscope.
Treating scabies cannot be done through OTC remedies; you will need a prescription-strength cream to eradicate this infection. You will then need to apply this cream or ointment directly onto the infected area. Your doctor may also prescribe a course of antihistamines and antibiotics to manage the itching and infections resulting from the open sores.
Granuloma inguinale
Granuloma inguinale is a rare sexually transmitted infection that causes chronic inflammation and scarring of the genitals. Also known as donovanosis, this infection results in blisters and lesions appearing on your genital and rectal areas. Fortunately, it is rare in the United States.
Diagnosing will require fluid from the sore and treatment through antibiotics (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or doxycycline).
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection caused by a poxvirus. You can get it from close physical contact, sexual contact, and sharing towels with a person who has the virus. They appear as itchy, red bumps that can occur as a cluster of as many as 20 of them. Open or damaged sores may spread the virus through the fluid that comes from them.
Molluscum contagiosum can be diagnosed through a visual examination, but your doctor may also take scrapings from the infected area to be sure. Typically, you will not require drastic medical intervention or treatments, as the condition can get better on its own in 6 to 12 months. However, doctors may also recommend that you get the blisters or bumps removed because they are extremely contagious.
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) is a sexually-transmitted bacterial infection caused by the Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria. It is a chronic infection of the lymphatic system. This infection can cause painful ulcers or sores to appear on and around your genitals, and some cases will require a course of oral antibiotics to resolve.
Suffering From Herpes Type 2 Outbreaks?
Herpezine is a specially formulated all-natural mixture of ingredients proven to help relieve and prevent HSV2 outbreaks when used as directed. This safe, over-the-counter Herpes treatment contains both traditional homeopathic and scientifically proven anti-viral ingredients such as L-Lysine HCI and Bee Propolis. Learn more about Herpezine on our website and visit our pricing page to purchase your first bottle.

About The Author
Terrence Tan Ting is an industrial engineer by profession but a full time writer by passion. He loves to write about a wide range of topics from many different industries thanks to his undying curiosity.